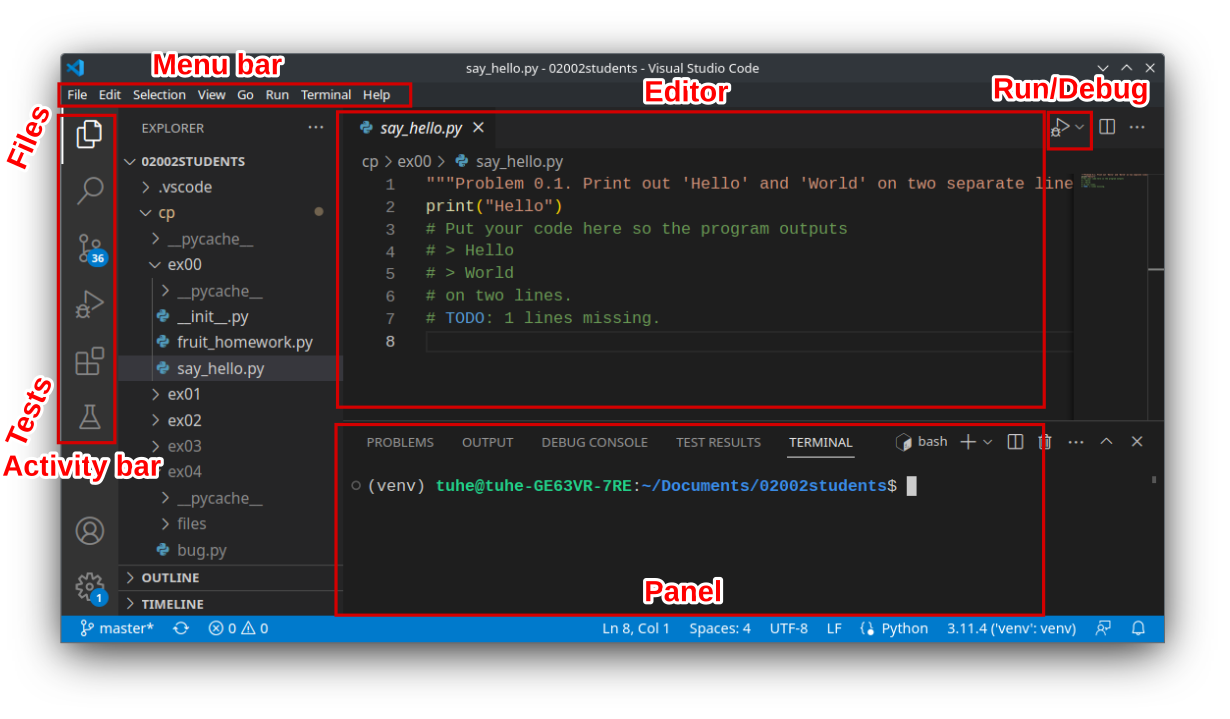
Using VS Code#
Note
VSCode is an IDE, which stands for Integrated Development Environment. Other popular IDEs for Python are Spyder and Pycharm. You can in principle use any of them if you choose, however, we can provide assistance with VSCode.
VSCode is the program we use to write and run Python code. It will not automatically make you a good programmer, however, it will help you a lot with mundane and annoying tasks, and that will in turn give you more time to learn to be a good programmer.
You can compare using VSCode to edit Python to using a textprocessor when you are writing a report, or using a fully equipped kitchen when you cook: Although you can in principle get the job done without these aids, better tools will as a rule allow you to accomplish more, and get a better result.
VSCode extensions#
Through VSCode it is possible to extend the functionality of VSCode by installing packages. These packages are called extensions and are found by clicking the four boxes above the tests in the Activity bar. For the functionality required for the 01001: Mathematics 1 course, you will need the Python extension.
Running commands in the terminal#
Note
The terminal is also sometimes called a shell, command line, or console. Apologies if we mix up the terms!
In the above screenshot, the terminal is open in the panel in the bottom of the screen. If the terminal is not shown, you can
immediately activate it by selecting from the menu bar. The terminal allows you to type in commands to your operating system
which will then be run in the current directory and display the result. Try for yourself by typing in the exact line python --version
$ python --version
Python 3.10.12
The tilde
The tilde in the front of the path means the location is relative to your home directory.
The blue text in the bottom-center pane tells you the current directory that the terminal is in: ~/Documents/02002students. Many of the commands you will use will behave differently in different directories.
You can always print out the current path by typing cd (Windows) or pwd on (Mac/Linux)
$ pwd
/builds/cp/02002students
To see the content of the directory, type dir (Windows) or ls (Mac/Linux). An example:
$ dir
README.md cp cp.egg-info requirements.txt setup.py
Try it yourself
Run the commands cd cp, cd ex00 and pwd. Then try cd .. and pwd
You can compare that to the actual directory using a file explorer.
The final command which you need to know is how to change directories. Use cd <directory name> (Windows/Mac/Linux) to go into a directory, and cd .. to go up one directory.
Starting the Python shell#
Hint
Press the up-button the keyboard to access previous commands. This is very useful if you make a typo in a command.
To start Python, type in python in the terminal. This will start Python and print the welcome message.
You can then input commands as described in the book, for instance:
>>> print("Good job!!")
Good job!!
>>> print("You are doing it!")
You are doing it!
The Python shell offers a way to quickly test the effect of single commands. We will use it extensively in the documentation to provide examples of what the programs do,
and you can always see when an example can be run in the Python shell because the lines start with >>>.
Running a Python file from the terminal#
Lets say you have a Python file you want to run from the terminal, for instance, this could be cp/ex00/say_hello.py. You can run it from the terminal:
- Calling any Python script
Change the directory to
02002students/cp/ex00using the commandcd cp/ex00(assuming you are already in the02002studentsfolder). Then run the file as follows$ python say_hello.py Hello World
- As a module (advanced)
From any directory, run the command:
$ python -m cp.ex00.say_hello Hello World
Note
You may wonder why the second (module) example works. The reason is that when you followed the installation guide, the command pip install -r requirements.txt registered
the directory 02002students/cp with Python. Put simply, whenever Python sees python -m cp.(etc. etc.), it knows it should look in the folder 02002students/cp/(etc. etc.).
If you are just working with a single file, many find that the first version is preferable.
However, if you have installed the folder as a package, that the python -m ... works no matter which directory you are running it in.